Unveiling the Art and Science of Architectural Model Making
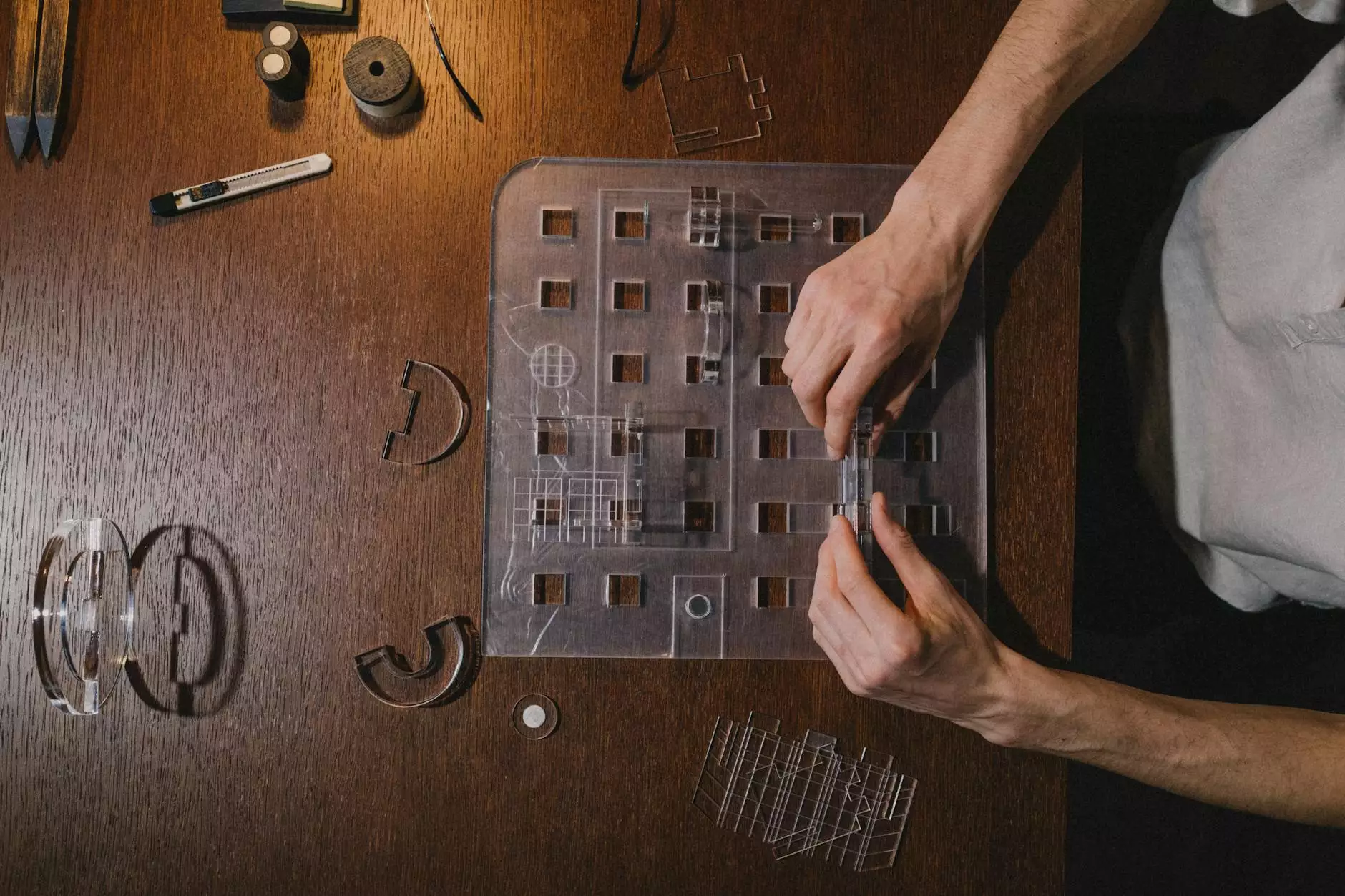

Architectural model making is a crucial component in the architecture and design industry. It serves as a tangible representation of an architect's vision, allowing for the exploration and communication of design concepts in a way that mere drawings and digital models cannot achieve. This comprehensive guide delves into the significance, techniques, materials, and advantages of architectural model making, equipping architects with the knowledge to elevate their design process and client presentations.
Understanding Architectural Model Making
The essence of architectural model making lies in its ability to bring an architect's imagination into a physical form. A model can illustrate a project's scale, proportions, and spatial relationships, making complex ideas accessible to clients and stakeholders. Below are some key points that highlight its importance:
- Visualization: Models facilitate a better understanding of design by showcasing three-dimensional spatial relationships.
- Communication: They serve as an effective communication tool between architects and clients, ensuring all parties share a common vision.
- Problem-solving: Building a model allows architects to experiment with design elements and address potential issues before construction.
- Marketing: High-quality models can attract potential clients, showcasing the architect's creativity and technical skill.
Materials Used in Architectural Model Making
The choice of materials in architectural model making significantly impacts the final product's quality and appearance. Here are some of the most common materials used:
1. Foam Board
Foam board is lightweight and easy to cut, making it an ideal choice for initial concept models. It provides a smooth surface for painting and detailing.
2. Basswood
Basswood is a favored material among professional model makers due to its strength, durability, and fine grain. It can be easily sanded and finished, allowing intricate detailing.
3. Cardstock
This is often used for quick models and prototypes. It is affordable and readily available, making it perfect for preliminary designs.
4. Acrylic/Plexiglass
Acrylic provides a modern aesthetic and allows for transparency in models, making it suitable for showcasing interior layouts and lighting designs.
5. 3D Printed Materials
With the advent of technology, 3D printing has transformed architectural model making. It allows for complex geometries and precise details that traditional methods may struggle to achieve.
Techniques in Architectural Model Making
The process of creating a model involves a variety of techniques that can vary based on the project's requirements and the materials used. Below are some prominent techniques:
1. Sketch Models
These models are used during the initial brainstorming phase. They focus on exploring general shapes and forms rather than detailed representation.
2. Presentation Models
These are highly detailed and polished models created for client presentations. They often incorporate landscaping and other contextual elements.
3. Working Models
Working models serve to test design concepts and can be utilized to convey functionality and usability during the design process.
4. Digital Models
While not physical, digital models play a critical role in modern design processes. They can seamlessly integrate with physical models, allowing for virtual simulations and presentations.
The Role of Architectural Models in Client Communication
Effective communication is paramount in the world of architecture. Architectural model making enhances this by serving as a visual aid that can bridge the gap between technical jargon and client understanding. Here's how models facilitate this process:
- Enhanced Understanding: Clients can visualize what the final product will look like, reducing ambiguity and fostering confidence in the architect's vision.
- Interactive Design Experience: Physical models allow clients to engage with the design physically, providing feedback and inspiring alterations in a hands-on manner.
- Collective Decision-Making: Models serve as a focal point for discussions, ensuring that every stakeholder's voice is heard during the design process.
Case Studies: Successful Architectural Model Making
Examining successful projects that relied on architectural model making can provide valuable insights into effective practices. Here are two illustrative case studies:
1. The Museum of Modern Art (MoMA) Expansion
In the expansion of MoMA, architects created intricate models to visualize the complex spatial relationships between the new wing and the existing buildings. The physical models facilitated discussions about light, space, and flow with stakeholders, leading to a more cohesive and functional design.
2. High Rise Residential Towers
During the design process for a series of high-rise residential towers in an urban area, architects utilized both physical and digital models. The physical models provided a tactile experience of the building's scale in relation to its surroundings, while digital models allowed for thorough analysis of environmental impacts, resulting in an optimized final design.
Challenges in Architectural Model Making
Despite its benefits, architectural model making is not without challenges. Some common issues faced by architects include:
- Time Constraints: The model-making process can be time-consuming, especially for highly detailed presentations.
- Budget Restrictions: High-quality materials and skilled labor can significantly increase project costs.
- Material Limitations: Some materials may not achieve the desired precision or aesthetic qualities required.
Future Trends in Architectural Model Making
As technology advances, the field of architectural model making continues to evolve. Anticipated trends include:
- Increased Use of Augmented Reality (AR): AR can overlay digital information onto physical models, allowing for interactive design experiences that can be easily shared with clients.
- More Sustainable Practices: As sustainability becomes increasingly important in architecture, there will be a shift towards using eco-friendly materials and practices in model making.
- Integration with Virtual Reality (VR): VR technology is set to enhance model making by providing immersive experiences within virtual environments.
Conclusion: The Enduring Value of Architectural Model Making
In conclusion, architectural model making remains an invaluable tool in the architect's arsenal, enhancing design processes, promoting effective communication, and ultimately contributing to successful project outcomes. By understanding its significance, employing various techniques, and staying abreast of emerging trends, architects can leverage model making to elevate their practice and bring their visions to life.
As you navigate the complexities of architectural design, remember that every innovative structure begins with a thoughtful model. Embrace the art of model making, and watch as your designs transform from concept to reality!